Anticodon of a Particular Trna Molecule is
Ribosomes link together amino acids and then release them to create a protein. Recognizing the structure of the mRNA bound to a tRNA the two subunits of the ribosome discussed below can combine to start synthesizing protein from the mRNA strand.
After the RNA folds into its tertiary structure it is L-shaped with the acceptor stem and T-arm forming an extended helix and the anticodon loop and D-arm similarly making another extended helix.

. Or equivalently one-half the amount in a diploid somatic cellFor simple diploid eukaryotes the term is often used interchangeably with genome size but in certain cases eg. C The aminoacids tRNA complex then comes to mRNA where adapter nucleotide triplet or anticodon of tRNA becomes attached with the complementary base triplet codon of mRNA. Transfer RNA tRNA is an adapter molecule that links a specific codon in mRNA with its corresponding amino acid during protein synthesis.
The transfer of aminoacids to tRNA is catalysed by the previous aminoacyl RNA synthetase enzyme itself Fig. After transcription and following synthesis RNA. The -COOH group of the complex binds to the -OH group at the terminal base triplet CCA at 3 end.
Each mature tRNA contains an average of 13 such modifications per molecule. A gamete of a particular organism or species expressed in number of base pairs or in units of mass typically picograms. There are numerous tRNA molecules that help to build a protein during this process.
Most amino acids have more than one codon that codes for them although methionine only has one. Interestingly this means that the tRNA anticodon has the RNA version of the same nucleotide sequence of the original gene. The first adaptor is the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase which couples a particular amino acid to its corresponding tRNA.
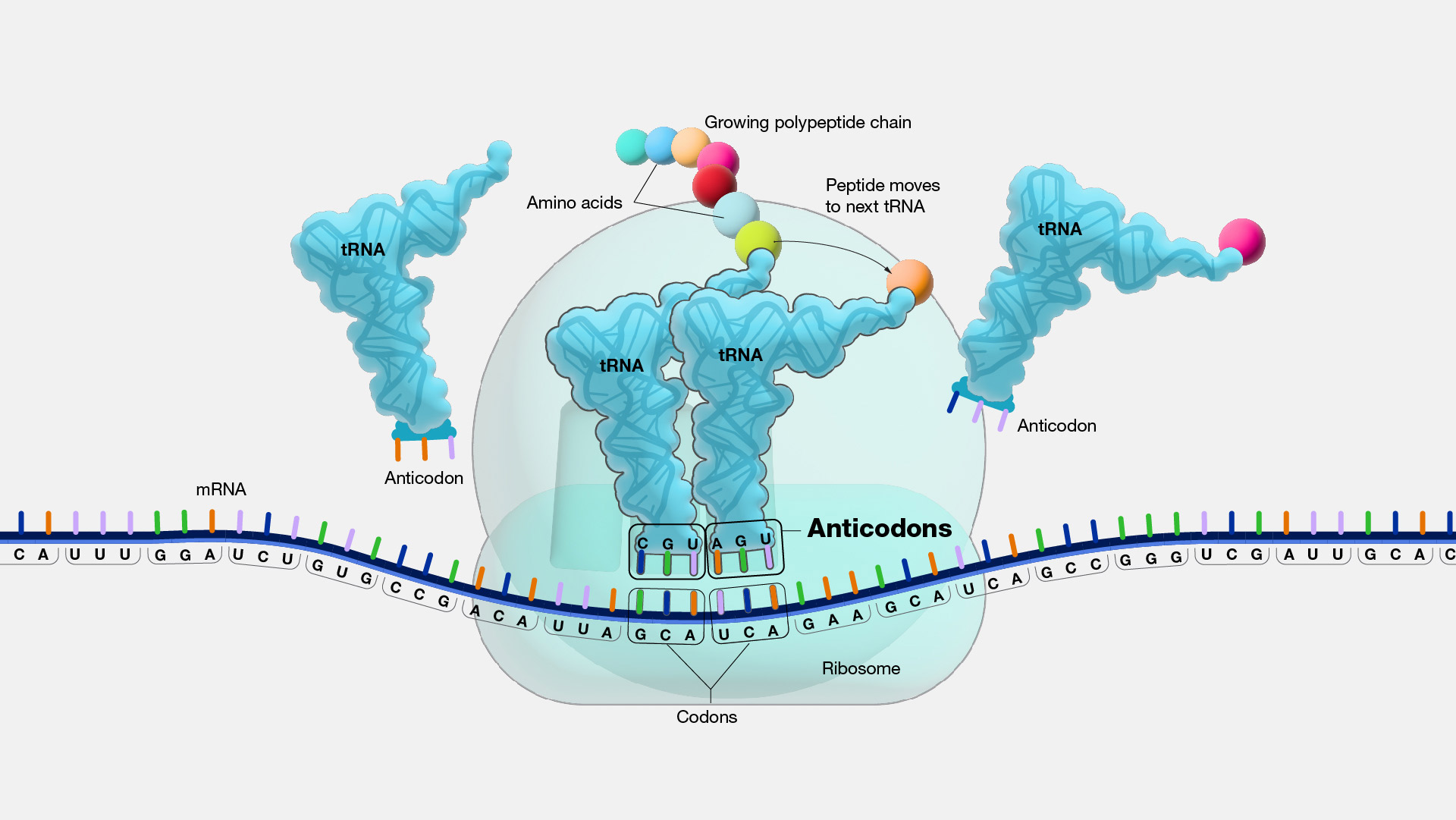
Codon A three-nucleotide sequence in an mRNA molecule that codes for a particular amino acid. The tertiary structure creates two double helices at right angle to each other. When the tRNA recognises its complementary codon in the mRNA strand it goes to collects its specific amino acid.
This particular tRNA carries a methionine amino acid. The tRNA molecule on the other hand has an anticodon which will match its complementary codon on the mRNA. Proteins are assembled from amino acids using information encoded in genes.
In fact one codon the codon is generated. As the tRNA molecule returns with the amino acid the anticodon of. Each protein has its own unique amino acid sequence that is specified by the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding this protein.
The tRNA contains a three-letter code on one side and carries a specific amino acid on the other side. A charged tRNA molecule along with its amino acid enters the ribosome at the A-site. The amino acid.
The attachment of amino acids to specific tRNAs is mediated by a group of enzymes called aminoacyl tRNA synthetases which were discovered by Paul Zamecnik and Mahlon. The genetic code is a set of three-nucleotide sets called codons and each three-nucleotide combination designates an amino acid for example AUG. RRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes.
Each amino acid added to the growing end of a polypeptide chain is selected by complementary base-pairing between the anticodon on its attached tRNA molecule and the next codon on the mRNA chain. A sup-tRNA is derived from a natural tRNA with the anticodon altered to base-pair with one of three stop codons UAG UAA or UGA and aminoacylated to participate in translation elongation at the. As a result aminoacyl-tRNA AMP and enzyme are formed.
This adapter molecule is called tRNA transfer RNA. Charging of tRNA. The anticodon loop makes bases complementary to the codes on the mRNA and amino acid end binds to the respective amino acids.
The tRNA plays the role of an adaptor and matches each codon to its particular amino acid in the cytopolasmic pool. An anticodon is a trinucleotide sequence located at one end of a transfer RNA tRNA molecule which is complementary to a corresponding codon in a messenger RNA mRNA sequence. The AA-AMP-E complex further reacts with a particular tRNA.
Ribosomal RNA rRNA not tRNA is a significant structural component of the ribosome. Its anticodon reads and binds to the complementary codon. The code on tRNA called an anti-codon must match the three-letter code called a codon on the mRNA already in the ribosome.
The same amino acid always coded by a particular codon. In cell biology the nucleus pl. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA rDNA and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form small and large ribosome subunits.
The opposite end of the tRNA molecule has a site where a specific amino acid can bind to. The other arm consists of DHU loop and anticodon arm with loop. Codons that each encode a specific amino acid to be added to the growing protein are found within the messenger RNA mRNA not the tRNA.
Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase aaRS enzymes then charge each mature tRNA with an amino acid on their 3 end a process. Transfer RNA serves as a link or adaptor between the messenger RNA mRNA molecule and the growing chain of amino acids that make up a protein. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid rRNA is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes essential to all cells.
Depending on the protein being built the next amino acid could be any one of the twenty. Transfer RNA abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA for soluble RNA is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length in eukaryotes that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. In this configuration uracil is sometimes referred to as pseudouracil Pseudouridine is the most abundant RNA modification in cellular RNA.
TRNAs are enzymatically modified post-transcriptionally. Pseudouridine abbreviated by the Greek letter psi- Ψ is an isomer of the nucleoside uridine in which the uracil is attached via a carbon-carbon instead of a nitrogen-carbon glycosidic bond. The incorporation of the correctly encoded amino acids into proteins depends on the attachment of each amino acid to an appropriate tRNA as well as on the specificity of codon-anticodon base pairing.
Thus it helps in protein synthesis. Every tRNA carries one anticodon and has one amino acid. RRNA is the physical and.
Each time an amino acid is added to the chain a specific tRNA pairs with its complementary sequence on the mRNA molecule ensuring that the appropriate amino acid is inserted into the protein being. This is where the ribosome comes in. The tRNA molecule is L- shaped.
Structurally the tRNA is an inverted L-shaped molecule which has an anticodon loop and amino acid acceptor end. The amino acid is bonded to the tRNA molecule by enzymes in the cytoplasm. A codon is a DNA or RNA sequence of three nucleotides a trinucleotide that forms a unit of genetic information encoding a particular amino acid.
C C-value The total amount of DNA contained within a haploid nucleus eg. TRNA contains anticodons not codons. Anticodons are basically the section of a transfer RNA t RNA is a categorization of three bases which are corresponding to codons in the mRNA.
From Latin nucleus or nuculeus meaning kernel or seed is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cellsEukaryotes usually have a single nucleus but a few cell types such as mammalian red blood cells have no nuclei and a few others including osteoclasts have manyThe main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear. The secondary structure of tRNA containing the acceptor region D- and T-arms and the anticodon loop is said to resemble a cloverleaf. The second adaptor is.
The particular amino acid that tRNA carries is determined by a three-letter anti-codon it bears. The tRNA has two properties. Transfer RNA tRNA does this by carrying an amino acid to the protein synthesizing machinery of a cell.
What Is The Anticodon Of Trna Molecules Quora

Anticodon An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Solved 21 The Anticodon Of A Particular Trna Molecule Is Complementary To The Corresponding Triplet In Rrna Complementary To The Corresponding Mrna Codon The Part Of Trna That Bonds To A Specific
No comments for "Anticodon of a Particular Trna Molecule is"
Post a Comment